Galaxy for TDM, latest achievements
For several years Galaxy project has been constantly growing and evolving. Having an active community, the new projects are running and new features are continuing to be developed. The dedicated series of blog posts will provide a short overview of the latest and most interesting ones from TDM perspective. The focus is on the areas of Galaxy servers’ network and resource sharing, cloud computation, HPC (high performance computing) and Machine Learning. All together these new features make Galaxy a good candidate for TDM computational platform for data intensive analysis, accessible not only for developers.
Galaxy Network
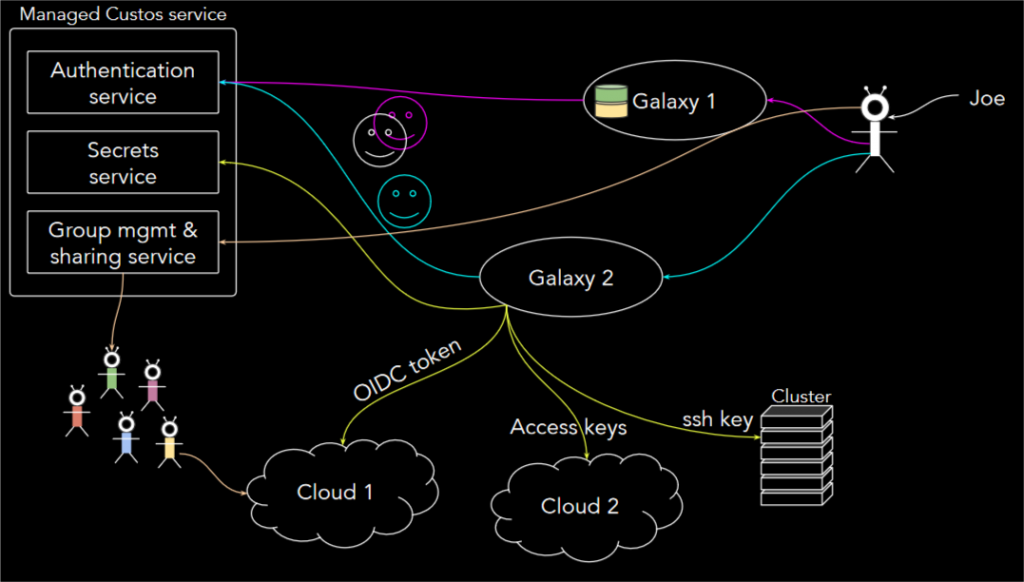
Custos
- Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA2.
- Indiana University, Bloomington, IN, USA3.
- Oregon Health and Sciences University, Portland, OR, USA
Custos, open source software that will provide science gateways such as:
- Galaxy with federated authentication;
- single sign-on across multiple science gateways, to allow a user to potentially access multiple Galaxy servers with a single identity;
- off-site group management;
- management of secrets such as access keys, cloud access keys and OAuth2 access tokens.
Pulsar
- Albert-Ludwigs-Universität, Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany
- Italian National Research Council, Bari, Italy
- CESNET, Prague, Czech Republic
- University of Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany
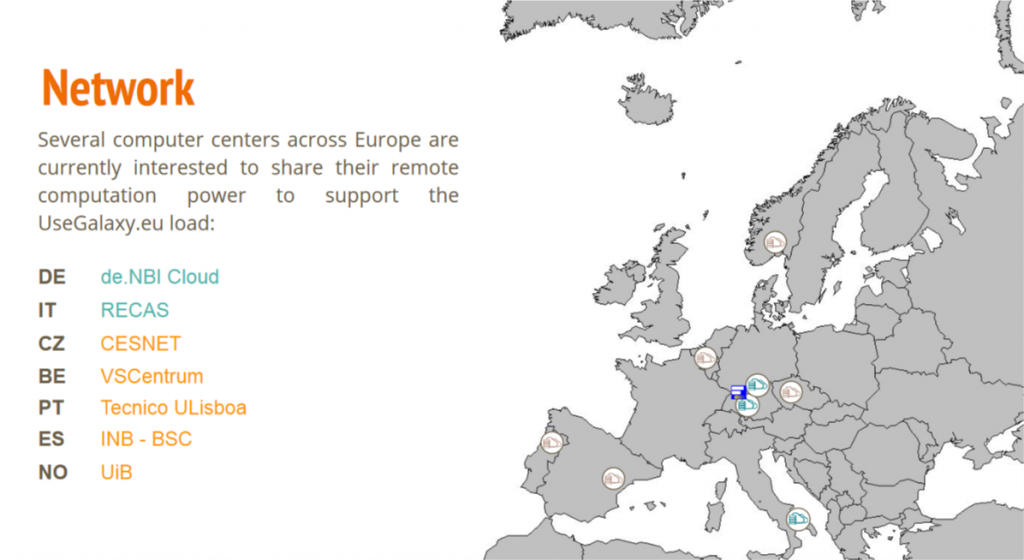
Several computer centers across Europe are currently interested in sharing their remote computation power to support the Usegalaxy.eu load: IT, UK, CZ, DE.
Pulsar project was founded to create this network of shared computational resources. As a result, Pulsar, a TES-like service written in Python that allows a Galaxy server to automatically interact with those remote systems, ensures that jobs and provenance information are correctly exchanged.